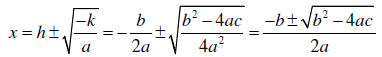Math 131: Essentials of Calculus
Vertex Form of the Quadratic: y = a(x - h)2 + k
Like the point -slope form for the equation of a straight
line which explicitly incorporates the
slope (m) and y-intercept (b) in the equation form, the vertex form of the
quadratic explicitly
incorporates information about the quadratic. Specifically
If a > 0 then the quadratic opens up; otherwise it opens
down
(h, k) are the coordinates of the vertex , the lowest (or
highest) point on the graph. This
yields the solution for quadratic max/min problems.
Note that the vertex form is: a times x minus h
squared plus k. The vertex is (h, k).
Example: The vertex form for the quadratic y = 2x2
+12x -8 is y = 2(x + 3)2 - 26 , a fact which
is easily verified by multiplying out the vertex form or by graphing both
equations (there should
be only one graph). Thus we know
The quadratic opens up as a = +2
(-3,-26) are the vertex coordinates. Since the graphic
opens up, this is the lowest point
on the graph – a global minimum.
How is the vertex form obtained? The underlying technique
is called “ completing the square ”.
Start with the vertex form, expand, equate coefficients, and solve for h and k .
1. Start with the vertex form and expand it using FOIL.
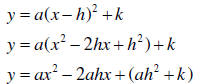
2. Equate this to the original quadratic y = ax2 + bx + c
; that is
y = ax2 + bx + c = ax2 - 2ahx + (ah2 + k)
3. Now the only way two quadratic equations can be the
same is if their coefficients
are the same. Equating coefficients yields three equations the first of which is
trivial
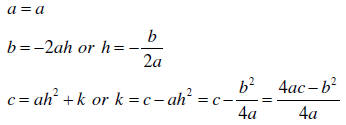
Note: I never memorize these formulas ; instead I multiply
out the vertex form of the quadratic,
equate coefficients and solve as is done in the example below.
Example: 2x2 +12x -8 = a(x - h)2 + k = ax2 -
2ahx + ah2 + k . Equating coefficients yields
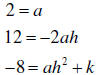
This is easily solved for h and k:
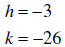
Thus y = 2x2 +12x -8 = 2(x - (-3))2 - 26 = 2(x + 3)2 -
26
Find zeros using the vertex form: Set y equal to 0
and solving for x. That is
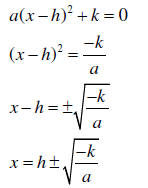
Example: Starting with y = 2(x + 3)2 - 26
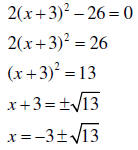
Note the plus or minus; the two zeros are easily verified
with a grapher.
Deriving the Quadratic Formula: Given that
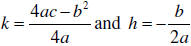 the roots of the
the roots of the
quadratic are given by 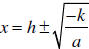 . Substituting in the
above values for h and k we obtain the
. Substituting in the
above values for h and k we obtain the
quadratic formula