• Linear equations .
• Geometrical interpretation.
• Number of solutions of a linear system.
• Solving linear systems by row reductions.
• Row-echelon form and reduced row -echelon form of a matrix.
• Matrix operations (addition, scalar mutiplication, multiplication in -
cluding block multiplication) and their properties ; matrix transpose.
• Matrix inverse: elementary matrices, finding matrix inverse, using in-
verses in solving linear syste ;
• Invertible Matrix Theorem.
• Scalar, diagonal, triangular and symmetric matrices and their proper-
ties.
• Determinants: evaluating by cofactor expansion.
• Determinants: properties ; evaluating by row reduction.
• Application of Determinants: Cramer’ s rule , inverse of a Matrix.
• Vector operation, norm, dot product.
• Projections, distance between a point and a line.
• Cross product: properties, applications (area of a parallelogram, volume of a
parallelepiped).
• Equations of a plane (normal vector and a point; three points.
• Parametric equations of a line.
• When planes intersect, are parallel, perpendicular.
• Distance between a point and a plane, two parallel planes.
Review Problems
1. Solve the following system of linear equations
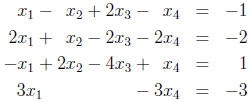
2. Use block product to find the product AB of the
following matrices
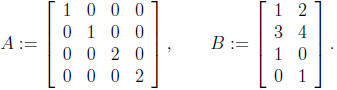
3. A is a 2-by-5 matrix and B is a 3-by-2.
(a) Is the product AB defind? If yes, state its size.
(b) Is the product BA defind? If yes, state its size.
4. Find the product CD of the following matrices
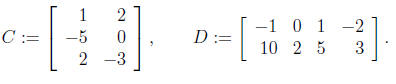
5. Find the inverse of the following matrix:
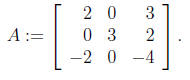
(a) using row reduction;
(b) using adjoint matrix.
6. Solve the following linear system :
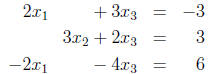
(a) using row reduction algorithm;
(b) using the inverse of the coefficient matrix ;
(c) using Cramer’s rule.
7. Consider the following matrix
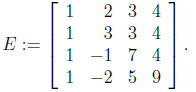
(a) evaluate the determinant of E;
(b) is this matrix E invertible? If yes, give the determinant of its
inverse E1
8. Find the components of the vector having initial point P1(−1, 0, 2) and
terminal point P2(0,−1, 0).
9. Find the distance between the points P1 and P2 above.
10. Find the components of the orthogonal projection of
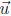 = (−1,−2) on
= (−1,−2) on
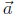 = (−2, 3).
= (−2, 3).
11. Find the angle between vectors 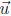 = (−1,−2) and
= (−1,−2) and
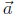 = (−2, 3).
= (−2, 3).
12. Find a vector perpendicular to the line 2x + 3y − 5 = 0.
13. Find the distance between the origin O = (0, 0) and the line 2x+3y −
5 = 0.
14. Find the components of a vector perpendicular to both vectors
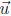 =
=
(1, 2, 0) and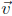 = (−2, 3, 0).
= (−2, 3, 0).
15. Find the area of a parallelogram defined by vectors
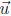 = (1, 2) and
= (1, 2) and
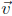 = (−2, 3).
= (−2, 3).
16. Find the volume of a parallelepiped defined by vectors
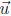 = (1, 2, 0),
= (1, 2, 0),
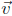 = (−2, 3, 0), and
= (−2, 3, 0), and
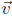 = (1, 1, 1).
= (1, 1, 1).
17. Find an equation of the line passing through the points P1(−1, 0, 2)
and P2(0,−1, 0).
18. Find an equation of the line passing through the point P1(0,−1, 0) and
parallel to vector (−1, 1, 2).
19. Find an equation of the plane passing through the point P1(0,−1, 0)
and perpendicular to vector (−1, 1, 2).
20. Find an equation of the plane passing through the points P1(−1, 0, 2),
P2(0,−1, 0) and P3(1, 1, 1).
21. Are the two planes 2x+3y −5z = 10 and 6x+9y −15z = 12 parallel?
Explain.
22. Are the two planes 2x + 3y − 2z = 10 and 5x − 2y + 2z
= 15 perpendicular? Explain.
23. Find the distance between the origin O = (0, 0, 0) and the plane 2x +
3y − 5z = 10.
24. Find the distance between parallel planes 2x + 3y − 5z = 10 and 6x +
9y − 15z = 12.